Understanding Health Insurance: A Deep Dive into Star Health & Niva Bupa
Star Health seems to offer a good risk-reward where things are expected to improve from a cyclical low point
It's always exciting to explore and understand new industries, and today, we delve into the health insurance sector. Health insurance is a critical financial product, offering protection against rising medical costs, yet its business model and valuation can be complex to grasp. To illustrate these concepts, we analyze India’s two pure-play health insurance companies: Star Health and Niva Bupa.
Business Model of a Health Insurance Company
A health insurer earns revenue primarily through premiums collected from policyholders. The profitability of this business depends on two key factors:
Underwriting performance (determined by the claims and expense ratios).
Investment income (returns earned on the float (premiums collected) but not yet paid as claims).
Key Metrics to Evaluate a Health Insurer:
Combined Ratio (CoR) = (Claim Ratio + Expense Ratio) / Net Earned Premium
Below 100%: Profitable underwriting.
Above 100%: Underwriting losses (relying on investment income for profitability).
Claims Ratio: Percentage of premiums paid as claims.
Expense Ratio: Operating costs as a percentage of net earned premium.
Solvency Ratio: Capital adequacy (higher is better for risk management).
Investment Yield: Returns earned on investment assets.
Now, let’s compare Star Health vs. Niva Bupa using these metrics.
Financial & Business Comparison: Star Health vs. Niva Bupa
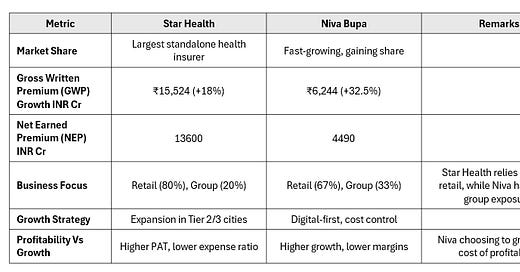
A. Scale & Market Positioning
The comparison between Star Health and Niva Bupa highlights a clear distinction in their strategies. Star Health, as the largest standalone health insurer, maintains a stronghold in the retail segment (80%) and focuses on expansion into Tier 2/3 cities, ensuring steady growth with better profitability. In contrast, Niva Bupa is aggressively scaling its business, growing premiums at a much faster rate (+32.5%), but at the cost of lower margins and higher expenses. While Niva Bupa’s digital-first and cost-control approach aims to capture market share, its reliance on group insurance (33%) adds volatility to claims. Star Health’s lower expense ratio and profitability-oriented approach provide stability, whereas Niva Bupa’s high-growth strategy remains a work in progress, requiring sustainable margin improvements in the future.
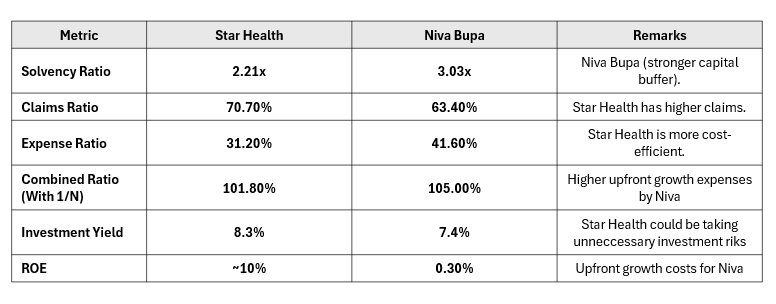
B. Financial Performance (9M FY25 Annualized)
The financial comparison between Star Health and Niva Bupa underscores key differences in their operating models and risk strategies. Niva Bupa maintains a stronger capital buffer with a higher solvency ratio (3.03x vs. 2.21x), allowing it to sustain aggressive growth. However, this comes at the cost of lower profitability, as reflected in its significantly lower ROE (0.30% vs. ~10%) and a higher expense ratio (41.6% vs. 31.2%). Star Health, on the other hand, demonstrates superior cost efficiency and higher investment yield (8.3% vs. 7.4%), though it carries a higher claims ratio (70.7%) and potential investment risks. The combined ratio further highlights Niva’s upfront growth expenses (105% vs. 101.8%), indicating that while it is prioritizing expansion, it needs to achieve better cost control for long-term profitability.
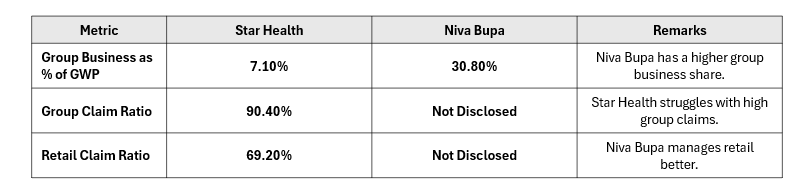
C. Group vs. Retail Business
Niva doesn’t disclose the claim ratio separately for group and retail which would have been useful in gauging its writing efficiency (whether growth is quality or just aggressive).
Valuations - Favorable Risk-Reward for Star
Star Health has already experienced a 60% drawdown from its peak due to various challenges that have impacted its profitability and growth trajectory. One of the most pressing issues is the high losses in its group insurance segment, where the claim ratio has reached 90.4%, significantly affecting overall underwriting margins. Additionally, the company faces intense competition in the health insurance market, with new players adopting aggressive pricing strategies, making it difficult to sustain market share without compromising profitability. Another hurdle is expense management, as despite having a lower expense ratio than some peers, Star Health still needs to optimize its cost structure to improve margins further. Furthermore, regulatory changes and pricing pressures from IRDAI require the company to continuously adapt its product pricing and underwriting policies, adding to operational complexities.
To address these challenges, Star Health’s management has devised a comprehensive turnaround strategy focused on improving profitability and operational efficiency. The company is actively tightening its underwriting policies in group insurance, implementing a risk-based pricing mechanism to control claim outgo. Additionally, it is leveraging technology-driven automation to streamline operations and enhance claims management efficiency. To improve cost control, the company is expanding its hospital partnerships to negotiate better treatment pricing, ultimately reducing claims expenses. At the same time, Star Health is diversifying its product offerings, introducing customized health plans targeting niche customer segments. It is also strengthening its distribution network, particularly in Tier 2/3 cities, while expanding digital and home healthcare services to improve customer engagement and reduce hospitalization rates. These strategic initiatives aim to enhance Star Health’s underwriting profitability and position it for sustainable long-term growth.
In contrast, Niva Bupa, with its already high valuation, faces a limited upside unless it can sustain extraordinary growth in an increasingly competitive market while also improving its key profitability metrics. Higher concentration on group would result in volatility in its claim ratios and hence will keep impacting the profits sustainability.
While both companies have strong positions in the growing Indian health insurance market, Star Health appears to offer a better risk-reward trade-off due to its superior cost structure, underwriting discipline, and reasonable valuation multiples. However, it must improve its group health profitability to sustain long-term growth. On the other hand, Niva Bupa is growing rapidly but trades at premium valuations, and any negative surprises could lead to a sharp correction, especially as early investors may look to exit post lock-in. Investors should weigh growth vs. profitability trade-offs carefully before making any decisions.
Important Note and Disclaimer: Please note that this note is shared only for the education purpose and in no way, it constitutes any buying or selling recommendation. We do not hold Star Health and Niva Bupa in our portfolio.
If you are interested in accessing our research and joining a network of well informed investors, please contact us at Gaurav.a@nineonecapital.in